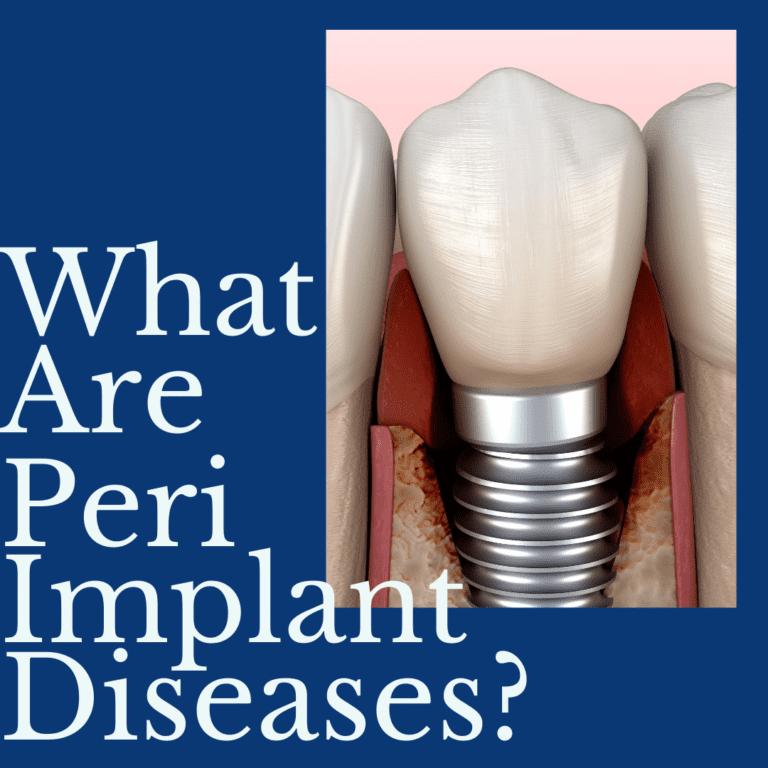
While the majority of dental implant procedures are successful, there are rare cases where complications can occur. One common complication associated with dental implants are known as peri-implant diseases, which are infections of the soft and hard gum tissues surrounding an implant. As a potential dental implant candidate, it is important to be aware of what peri-implant diseaes and how they can affect your dental implant treatment outcomes.
For starters, peri-implant diseases are caused by an accumulation of bacteria along the gum line and base of the implant. This can be the result of poor oral hygiene, diabetes, smoking, or a history of periodontitis. Excess bacteria along the gum line irritate the gum tissue and cause inflammation, much like how gum disease forms around natural teeth. In fact, peri-implant diseases can progress in a way that is similar to gum disease as well.
Just as gum disease has two forms and can progress from its mild form to its advanced form, peri-implant diseases also have two forms:

Peri-implant mucositis is comparable to gingivitis in that it causes inflammation only in the soft tissues surrounding the dental implant. Like gingivitis, peri-implant mucositis does not cause bone loss and can be reversible if caught early. If not treated, peri-implant mucositis will progress into peri-impantitis.
Peri-implantitis is comparable to periodontitis in that it causes inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the dental implant, as well as bone deterioration. It can cause dental implant failure and usually requires surgical intervention as treatment.
Since bone deterioration significantly increases the risk of dental implant failure, early detection of peri-implant mucositis is the key to preventing peri-implantitis. The symptoms of peri-implant mucositis are similar to those of gingivitis and include: redness, swelling, and inflammation of the gum tissue. As a result of inflammation, you may notice that your gums feel tender or that they bleed easily while brushing or flossing. Any of these signs is an indication that you should immediately schedule an appointment with your implant dentist to determine if an infection is present.
Although peri-implantitis will also have symptoms such as redness, swelling, and inflammation, it will also be accompanied by bone loss around the implant. Despite the fact that peri-implantitis is often viewed as comparable to periodontal disease, it has one main difference. While periodontitis can usually be diagnosed from radiographs alone, some cases of peri-implantitis may not be detected by radiographs and may only be diagnosed through the use of CBCT imaging. This is because bone loss can occur on the facial or lingual sides of the implant, which is only visible when a CBCT scan is used. To successfully diagnose peri-implantitis, it is recommended to do a baseline scan immediately following the placement of dental implants that can be used as a reference in the future to determine if bone loss has occurred.
Overall, peri-implant diseases can affect the soft and hard tissues surrounding a dental implant and can increase the risk of implant failure. They are most often caused by poor oral hygiene, diabetes, smoking, and a history or periodontal disease, therefore they can be prevented by managing these conditions appropriately. For the best treatment outcomes, it is recommended to schedule an appointment with your implant dentist as soon as any signs of peri-implant mucositis occur such as redness, swelling, or inflammation. The early diagnosis and treatment of peri-implant mucositis is the best way to prevent peri-implantitis.

Irfan Atcha, DDS, DICOI, DADIA at New Teeth Chicago Dental in Chicago, Illinois is a board-certified general dentist and a nationally recognized expert in dental implants, cosmetic dentistry, and sedation dentistry.