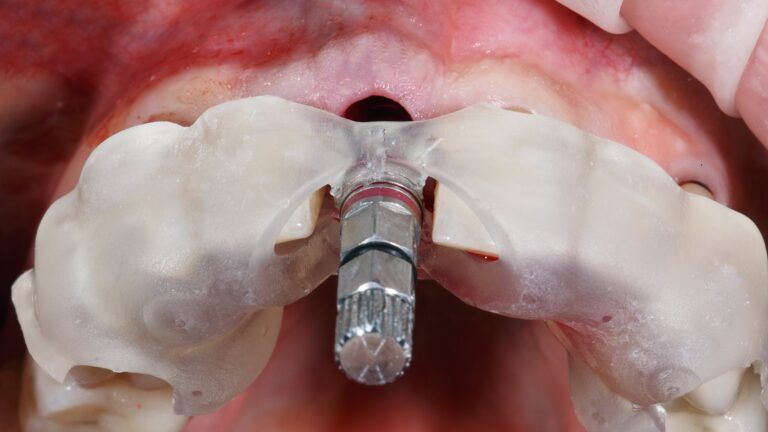
If you are considering dental implants, it’s important to be aware of the risks associated with peri-implant diseases. This type of disease can occur after having dental implants placed, and can affect their longevity. In this blog post, we will discuss what peri-implant diseases are, the risk factors involved, and ways to prevent them from occurring.
What are Peri-Implant Diseases?
Peri-implant diseases are infections that occur around the area of dental implants. There are two types of peri-implant disease: peri-mucositis and peri-implantitis.

- Peri-mucositis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane (gums) around the implant. This can make the gums appear red and swollen, and they may be tender to the touch or bleed easily. Peri-mucositis can develop into peri-implantitis when not treated, however treatment can also reverse this condition.
- Peri-implantitis is a more serious infection that causes inflammation of the gums, as well as deterioration in the bone around the implant. In addition to the aforementioned symptoms, peri-implantitis is also characterized by gum recession that exposes the underlying implant threads, pus around the gums, and loosening of the implant. Peri-implantitis almost always requires surgical treatment.
Both of these diseases can lead to loss of the implant if left untreated. Peri-implant diseases can cause implant failure in a few ways. The infection can cause the implant to loosen, and eventually it may fall out. The infection can also cause the bone around the implant to deteriorate, which can make the implant become unstable. In addition, the infection can damage the gums and surrounding tissue, which can make it difficult to place a new implant in the future.
When diagnosing these conditions, a visual exam, radiographs, and a CBCT scan are usually taken. The visual exam can help to assess the implant, gums, and surrounding bone for any signs of infection or inflammation. Radiographs can also be helpful in detecting any changes in the bone around the implant, however they are not always able to provide an adequate image. For this reason, a CBCT scan is often used to get a more detailed view of the area around the implants, and can help to determine if there is any bone loss. The presence of bone loss allows your dentist to determine if it is peri-mucositis or peri-implantitis.
Risk Factors
Because of the potential risks associated with peri-implant diseases, it’s important to be aware of the risk factors involved. There are a few different risk factors that have been identified:
- Poor oral hygiene: This is by far the most important risk factor for peri-implant diseases. Plaque and bacteria build-up around the implant can lead to inflammation and infection. It’s important to brush and floss regularly, as well as see your dentist for regular cleanings.
- Smoking: Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of peri-implantitis. This is likely due to the fact that smoking decreases the blood supply to the gums, which can make it more difficult for them to heal.
- Alcohol consumption: Alcohol consumption has also been shown to increase the risk of peri-implantitis. This is likely because alcohol dries out the mouth, which can lead to a decrease in saliva. Saliva is important because it helps to keep the mouth clean and free of bacteria.
- Systemic conditions: Certain systemic conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of peri-implantitis. This is likely due to the fact that these conditions can decrease the body’s ability to fight infection.
How to Prevent Peri-Implantitis
Now that we’ve discussed what peri-implant diseases are and the risk factors involved, let’s talk about ways to prevent them. The following tips can help you significantly decrease the risk of developing peri-implant diseases:
Practice Good Oral Hygiene
The best way to prevent peri-implantitis is to practice good oral hygiene. This is because plaque and bacteria that accumulate along the base of the implant are the main cause of these diseases. Be sure to brush at least twice a day, floss daily, and see your dentist for regular cleanings. These habits help to remove excess plaque and bacteria, which reduces the amount that can accumulate around the base of the implant. This makes it less likely that an infection will occur.

Regular Dental Exams
Another way to prevent peri-implantitis is to see your dentist regularly for exams and cleanings. This will allow your dentist to catch any problems early and treat them before they become serious. It is recommended to see your dentist at least once every six months for an exam and cleaning, however your dentist may have you come in more frequently if you are at an increased risk of developing a peri-implant disease. For example, some people may produce more plaque and require more frequent cleanings.
Stop Smoking
As we mentioned earlier, smoking is a risk factor for peri-implantitis. Smoking and other forms of tobacco can cause a variety of oral health problems and impair the mouth’s ability to stay healthy. If you smoke or use any type of tobacco, quitting is the best way to decrease your risk. In many cases, your implant dentist will have you quit smoking before they will perform implant surgery.
Manage Alcohol Consumption
As we mentioned earlier, alcohol consumption can also increase the risk of peri-implantitis. Excess alcohol consumption is associated with dry mouth, which can make it easier for bacteria to spread throughout your mouth. If you drink alcohol, it’s important to do so in moderation and try drinking water after finishing an alcoholic beverage to rinse away the alcohol and prevent bacteria from spreading.
Manage Systemic Conditions
Finally, if you have a systemic condition, such as diabetes, it’s important to manage it properly. This means following your doctor’s instructions and taking any medications that are prescribed. Since your oral health is so closely related to your overall health, having problems with one can inevitably lead to problems with the other. This means that taking care of your overall health can benefit your oral health and vice versa.
In Conclusion
In this blog, we discussed peri-implant diseases such as peri-mucositis and peri-implantitis, their risk factors, and ways to prevent these diseases from developing. Remember, practice good oral hygiene, see your dentist regularly for exams and cleanings, stop smoking, manage alcohol consumption, and manage any systemic conditions that you may have. By following these tips, you can significantly decrease your risk of developing peri-implantitis.
We hope that this information has been helpful and that they will help you take the necessary steps to prevent peri-implant disease. If you have any concerns, be sure to discuss them with your dentist.

Irfan Atcha, DDS, DICOI, DADIA at New Teeth Chicago Dental in Chicago, Illinois is a board-certified general dentist and a nationally recognized expert in dental implants, cosmetic dentistry, and sedation dentistry. Dr. Atcha is now serving patients in Naples, Bonita Springs and SW FL area with All-on-4 implants, teeth-in-a-day, same day dental implants and the complex zygomatic dental implants for the no-jaw bone solution approach. To schedule a consultation please email Dr. Atcha at teethforyou@gmail.com.